Describe the Dissolving Process at the Molecular Level
As we saw in Section 91 Solutions this means that substances must have similar intermolecular forces to form solutions. In molecular nature similar solute molecules are.
How Does A Solute Dissolve In A Solvent Solutions Chemistry Don T Memorise Youtube
How would you describe the dissolving process at the moleculer level by using the concept of random molecular motion.
. The concept of dissolving is when a solid called a solute completely mixes with a liquid called a solvent at the molecular level to become a single visible phase and become a homogeneous mixture. As the copper ions dissolve into the water they form a coordination complex with salts already present. Dissolving needs another term to be used this is solvation.
Students see that a liquids ability to dissolve a substance is a characteristic property that can be used to identify the liquid. The solvent particles must move apart to make room for solute particles. They should also note that water.
Describe on a molecular level the difference between the two physical changes melting and dissolving Step-by-step solution Chapter 33 Problem 3E is solved. Use the dissolution of a solid in a liquid as an example. The answer depends in part on the solute but there are some similarities common to all solutes.
Can you please give one example. Students look at illustrations and animations of these substances on the molecular level and see that the process of dissolving involves the attraction and interaction of the molecules of the liquid and the solid. The relative magnitudes of the energy changes.
This process requires energy to overcome forces of attraction between solvent particles. The answer depends in part on the solute but there are some similarities common to all solutes. Describe what happens on the molecular level as the water dissolves in the isopropanol.
The first step in the dissolving process is endothermic. Briefly describe the solution process at the molecular level. This helps the solvated molecule be soluble in the solvent.
Students know how to describe the dissolving process at the molecular level by using the concept of random molecular motion Materials. Solute particles occupy position which are normally occupied by solvent molecules. Dissolving a solid in a liquid depends on the interactions and attractions between the molecules of the liquid solvent and the particles of the solid solute.
The concentration of the solution is the amount of solute in a given amount of solvent. Solvation is briefly surrounding of solvent molecules around solute molucule. The concept of dissolving is when a solid called a solute completely mixes with a liquid called a solvent at the molecular level to become a single visible phase and become a homogeneous.
The kinetic molecular theory describes the motion of atoms and molecules and explains the properties of gases. Explanation of principles involved. Molecular view of the solution process - When solute dissolves in solvent particles of the solute disperse throughout the solvent.
Copper plating is the process of plating a layer of copper electrolytically on the surface of an item. Problem 3 Easy Difficulty. When a soluble solute is introduced into a.
Have students draw a model of water dissolving salt on the molecular level. At the molecular level the individual solid molecules become separated and interact less with each other and more with surrounding solvent molecules. As we saw in Section 91 Solutions this means that substances must have similar intermolecular forces to form solutions.
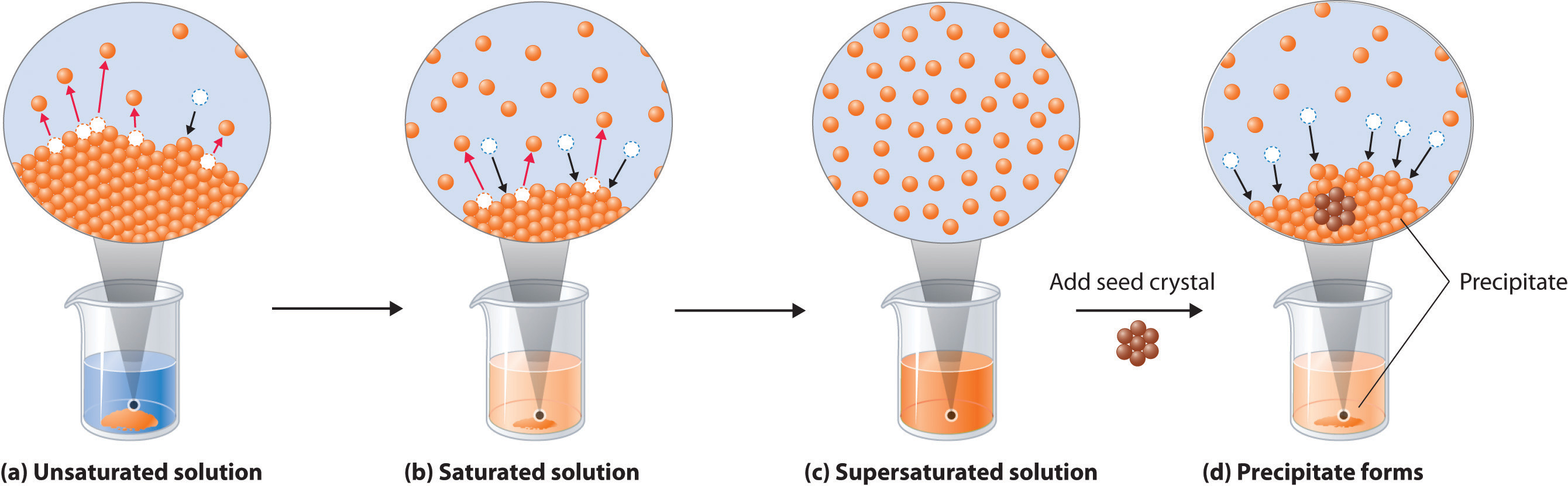
The copper then physically flows to the item where it is reduced to the metallic state by gaining. As illustrated in Figure 3 the formation of a solution may be viewed as a stepwise process in which energy is consumed to overcome solute-solute and solvent-solvent attractions endothermic processes and released when solute-solvent attractions are established an exothermic process referred to as solvation. Be sure to level and zero the unit.
Dissolving happens when the attraction between the particles of the solvent and solute are strong enough to overcome the attraction of the particles of the solute for one another. At the molecular level the individual solid molecules become separated and interact less with each other and more with surrounding solvent molecules. Eventually the particle detaches from the remaining solute surrounded by solvent molecules in solution.
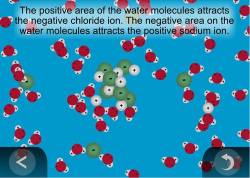
Students should state that the sodium ions are positively charged and the chloride ions are negatively charged. Up to 24 cash back There are 3 steps to the dissolving process. The solute particles must separate form the other solute particles.
In the case of molecular solutes like glucose the solute particles are individual molecules. Recall the rule that like dissolves like. Sodium chloride NaCl dissolves when water molecules continuously attack the NaCl crystal pulling away the individual sodium Na and chloride Cl ions.
This nonstop attack continuous until the whole NaCl crystal disintegrates. The concept of dissolving is when a solid called a solute completely mixes with a liquid called a solvent at the molecular level to become a single visible phase and become a homogeneous mixture. Dissolution is the noun form of the verb dissolve which most commonly means to mix into and melt within a liquid but has several other meanings including to break apart.
So a solvent film occurs around the molecule in other wordsa solvent-like micro-environment is formed. The process of a solute dissolving in a solvent is called dissolution dissolving. When a solute dissolves the individual particles of solute become surrounded by solvent particles.
Recall the rule that like dissolves like. What occurs at the molecular level to cause a solute to dissolve in a solvent. What occurs at the molecular level to cause a solute to dissolve in a solvent.
To understand this process at the molecular level we must apply the three steps we previously discussed. Dissolution generally refers to the process of dissolving or breaking apart. When a soluble solute is introduced into a.
Is a solution which can dissolve more solute. On the Activity Sheet have students describe what happens during the dissolving process when water dissolves salt.
Solubility And Molecular Structure

Dissolving And Back Again American Chemical Society

Dissolving Process Chemistry For Non Majors

Dissolving And Back Again American Chemical Society
How Does Sugar Dissolve In Water At A Molecular Level Quora
11 1 The Dissolution Process Chemistry
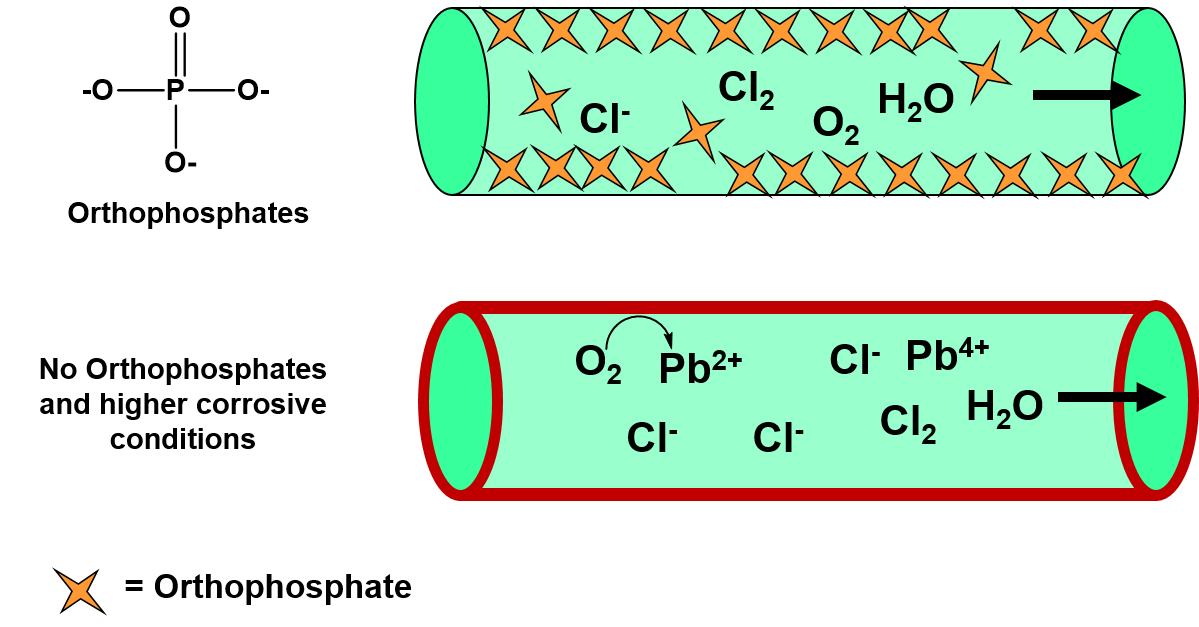
Ch104 Chapter 7 Solutions Chemistry

Dissolving And Back Again American Chemical Society

Dissolution Process An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
2 2 Water Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition

Research Reveals How An Acid Dissolves Molecule By Molecule Eberly College Of Science

Solutions And Solubility Ppt Download

Dissolving Process Ms Jonasson S Classes

4 1c Solution Chemistry Describe The Dissolving Process Cset Study Guide Chemistry
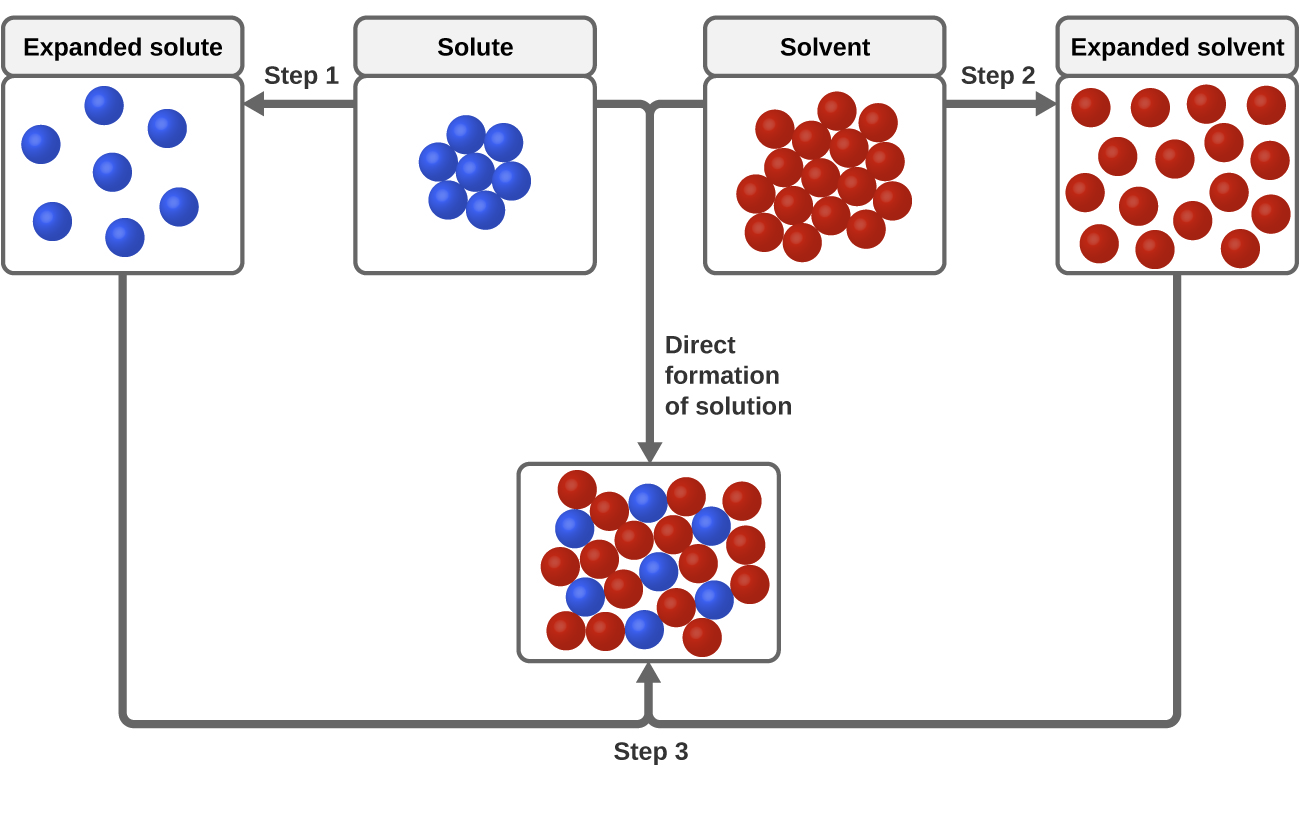
11 1 The Dissolution Process Chemistry

How Do Aqueous Solutions Of Ionic Molecular Compounds Differ Study Com
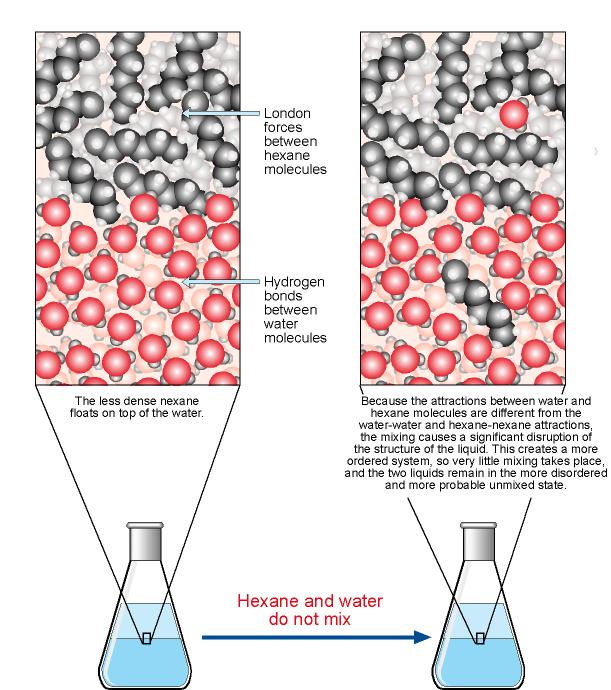
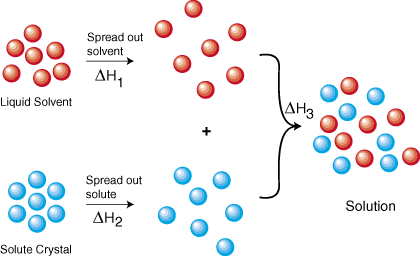
Comments
Post a Comment